Search is a very big part of almost every SharePoint site but searching through the content is not the goal, finding the correct content is. In this post I will give 8 tips to get better search results!
1 Refinement panel
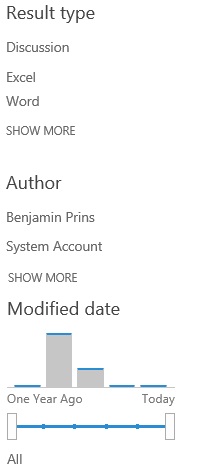
Use the refinement panel on the search results page to narrow down the results. When SharePoint displays the search results you can filter the results by using the refinement panel. Common refinement options are result type, author and modified date.
2 Use Boolean operators
Boolean operators are used to narrow or expand the search results. Capitalization usually does not matter in search, except for operators. For Boolean operators to work correctly they need to be written in capitals.
| AND | Use AND to narrow your search results. The returned search results include all of the free text expressions |
| NOT | Use NOT to narrow your search results. The returned search results don’t include the specified free text expressions or property restrictions. |
| OR | Use OR to expand your search to include more terms. The returned search results include one or more of the specified free text expressions or property restrictions. |
Example: “Project plan” OR “Business Case”
3 Use wildcards
Use a wildcard * if you want to be sure to get variations of the term you are looking for or if you are not sure about the spelling.
Example: Project* to search for all item starting with the word project.
4 Use double quotes
Use double quotes “” to find exact phrases if you are sure about the phrases.
Example: “Progress report”
5 Use Search shortcuts
SharePoint search has a few handy shortcuts that make searching for specific types of content faster and easier. When using a shortcut SharePoint combines property filters to narrow down the search results. When searching for a document called Projectplan search for projectplan doc instead of projectplan. In the background SharePoint will change the search shortcut from doc into filetype:doc OR filetype:docx, filtering the results and displaying only Word documents.
| Search shortcuts | Result |
| Deck or decks | Only PowerPoint presentations will be shown |
| Slide or slides | Only PowerPoint presentations will be shown |
| Doc | Only Word documents will be shown |
| Video | Only video files will be shown |
| Site | Only SharePoint sites will be shown |
| Blog or blogs | Blog sites will be shown |
| Post | Only shows the news feed activities |
| Conversation | Only conversations (discussions) will be shown |
6 Use Specifying properties
The most easy way to explain what properties are is to use the less technical term SharePoint uses which is; metadata. Metadata is the data captured to describe the content. By default SharePoint captures a lot of metadata such as document title, document type, last modified date. The main purpose of using metadata is to make sure all the content stored in SharePoint can be found easily.
A basic property restriction consists of the following three parts: a property name a operator and a value.
<Property Name><Property Operator><Property Value>
Example: Author:John or Title:Projectplan
7 Use Property restrictions (operators)
When using properties to narrow down the search results it is possible to make the search query even more specific with the use of different property restrictions. The most used and best known is the : operator. When using the : operator the returned results will all be equal to the specified value . There are a lot more operators available a few examples are:
| Operator | Description | Example |
| : | Returns results where the value is equal to the property value (short description) | Author:John |
| = | Returns results where the value is equal to the property value | Title=Projectplan |
| < | Returns results where the value is less then the property value | Created>9/20/2012 |
| > | Returns results where the value is greater then the property value | Modified<10/10/2012 |
Search in SharePoint 2013 supports several new property operators. See the full list of the property operators on Keyword Query Language (KQL) syntax referene table 2.
8 Try again
If you did not find the correct document, change the search query a bit. Add or remove terms, operators and properties. Not all documents will be found with the first attempt.
If you want to know more about the new search features check out the post SharePoint 2013 new search features.
Supporting links

Awesome! Better than Microsoft Reference !Thank you!
May I use excerpts from this post in a fact sheet? Of course I will credit you as the source and also offer a link to your site.
Yes you may as long as you will credit me and link the source 🙂
So I created some managed properties of Date/Time type and within my KQL statement, I’m trying to say ManagedProperty>{Today-1} and SP keeps saying incorrect Syntax. But I can do Created>{Today-1}. I’ve tried changing my Managed Properties over to text fields and formatting the date, tried date/time date only, date/time date+time – just cannot figure this out for the life of me. Any thoughts on the matter?
Nice Article! amazing that such a short, to-the-point list could be so useful and clear. It’s like the info.
Very good and Knowledgeable information
I would like to thank you for the efforts
you have made in writing this interesting and
knowledgeable article.
There is more relative topics below :
Independence Day